The economy is decarbonizing. Updates to the the world’s two most widely-used scope 3 emissions databases—USEEIO (US Environmentally-Extended Input-Output) and CEDA (Comprehensive Environmental Data Archive)—show a median 2% decrease in corporate emissions per dollar spent in the last year, reflecting global economic and energy changes and further signaling that business growth and emissions growth can be decoupled. While this reflects global progress, it is less than what’s needed to meet Paris-aligned corporate targets, which typically require at least 6% annual reductions in emissions intensity.
The updated data came from USEEIO and Open CEDA, which are managed by Cornerstone, a sustainability data collaboration between Watershed, the Sustainable Solutions Lab at the Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability, and ERG. The new versions of the databases are available today on cornerstonedata.org.
“The driving force of global decarbonization is economic value. The transition to renewable energy, improvements in operational efficiency, and the growth of sustainable products are all paying dividends, and the economy is decarbonizing accordingly.”
Michael Steffen, head of climate analytics at Watershed.
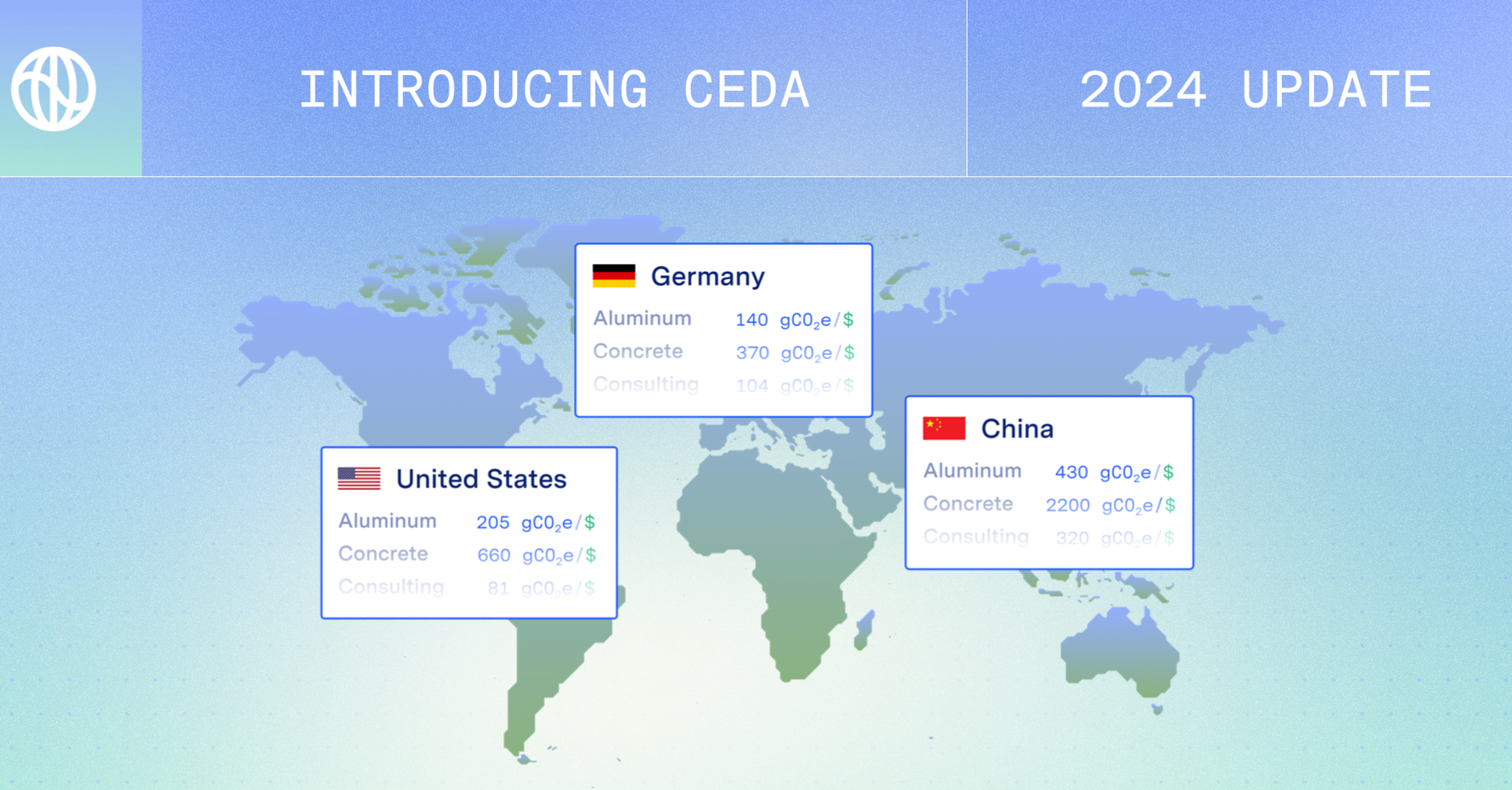
The two databases show slightly different values for the decarbonization of different companies: When applying this year’s updates to a test group of companies, Cornerstone found that the CEDA update resulted in a 2.0% median decrease in footprint size, and the USEEIO update resulted in a 1.8% median decrease. USEEIO is an emissions dataset specific to the United States, whereas CEDA is an emissions dataset representing 148 countries including the United States, which is why the two results differ slightly. The reported reductions account for inflation, so they represent real improvements in the emissions intensity of business activities.
The largest drivers of changes in both models were related to the electricity (driving 31% of the change), oil and gas production (driving 7% of change), and transportation sectors, which impact the supply chains of many industries.
Together, USEEIO and CEDA are used to calculate roughly 65% of scope 3 corporate carbon measurements globally. Each dataset is updated annually and uses data from the most recently available complete data year.
Cornerstone launched in August of this year, and this marks its first regular update of USEEIO and CEDA. In the coming months, the two databases will be merged to become the world’s most comprehensive dataset of Scope 3 spend-based GHG emissions factors. Learn more at cornerstonedata.org.